The vocoder was originally developed in the 1930s for telecom. It wasn't till later on that it became significant in music production – eventually transforming iconic sounds in all sorts of genres.
At its core, the vocoder analyzes the frequency content of a modulating signal (usually speech or vocals) and applies it to a carrier signal (often a synthesizer or other sustained tone).
The vocoder has transformed human voices into musical instruments since the 1970s, shaping modern music from Daft Punk's robotic "Harder, Better, Faster, Stronger" to Imogen Heap. Let's explore how vocoders work and create those iconic robotic vocals. You’ll get to know the key parameters and find the perfect tools – both plugins and hardware.
We want you to choose the right tools for your setup so you can get right away.
You Will Learn:
- How vocoders transform voices using modulator and carrier signals
- Essential parameters for shaping your vocoder sound
- Differences between analog and digital vocoder options
- Top plugins and hardware choices for every budget
- Professional techniques for creative vocoder effects
What Is a Vocoder and How Does It Work?
A vocoder, or "voice encoder," is an audio tool that blends one sound's tone (the modulator) with another's rhythm (the carrier). To make things simple – it makes your voice sound robotic or like a synthesizer.
Key Components of a Vocoder
The modulator is typically your vocal track, providing all the spectral content. The carrier, on the other hand, is usually a synth that gives the dynamic shape. Then, you've got analysis and synthesis filters that pull apart and piece back together these audio signals to create your final sound.
Now, let's break down the key components.
- Modulator: Usually a vocal track, providing the spectral content.
- Carrier: Typically a synthesizer, providing the dynamic envelope.
- Analysis and Synthesis Filters: These filters break down and reconstruct the audio signals.
How Does a Vocoder Work?
The vocoder functions by splitting the modulating and carrier signals into multiple frequency bands using filters. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
- Analysis of the Modulating Signal:
- The modulating signal (e.g., a vocal track) is divided into several frequency bands.
- Each band's amplitude is tracked over time to capture the speech or vocal characteristics.
- Carrier Signal Processing:
- Simultaneously, the carrier signal (a synth tone, for example) is split into matching frequency bands.
- Amplitude Modulation:
- The amplitude envelopes of the modulating signal are applied to the carrier's frequency bands.
- This imprints the vocal characteristics onto the carrier sound.
- Reconstruction:
- All processed bands are summed together to produce the final vocoded sound.
The essence of a vocoder lies in its ability to "speak" or "sing" through another sound, resulting in a robotic and musical effect.
Types of Vocoders: Analog vs. Digital
You've got your modulator (usually your voice) and your carrier (often a synth). Analog vocoders give you a warm sound, while digital gives you precision. Key parameters like band count and formant shifting are your best friends for perfecting the sound.
Analog Vocoders
Analog vocoders use physical circuits to process audio signals. They often have a warmer, more organic sound but can be less precise than their digital counterparts.

Digital Vocoders
Digital vocoders use software algorithms to achieve the same effect. They offer more control and flexibility, making them popular in modern music production.
Vocoder Parameters: What You Need to Know
When you're tweaking your vocoder, pay attention to parameters like band count (more bands mean better quality but more CPU usage), envelope followers, and formant shifting. These help shape your sound.
Here are the key parameters to focus on:
- Band Count: The number of frequency bands used to analyze and synthesize the signal. More bands mean higher fidelity but require more CPU power.
- Envelope Followers: Control how the carrier signal's envelope is applied to the modulator.
- Formant Shifting: Adjusts the formants (resonant frequencies) of the modulator, changing the perceived vowel sounds.
- Unvoiced Detection: Helps the vocoder distinguish between voiced (e.g., vowels) and unvoiced (e.g., consonants) sounds for clearer articulation.
Best Vocoder Plugins
Check out plugins like iZotope VocalSynth 2 and Waves OVox for top-notch digital options.
1. iZotope VocalSynth 2
iZotope VocalSynth 2 VocalSynth 2 is a powerful vocal processing plugin that includes a vocoder module. It offers advanced features like formant shifting and unvoiced detection, making it a top choice for producers.
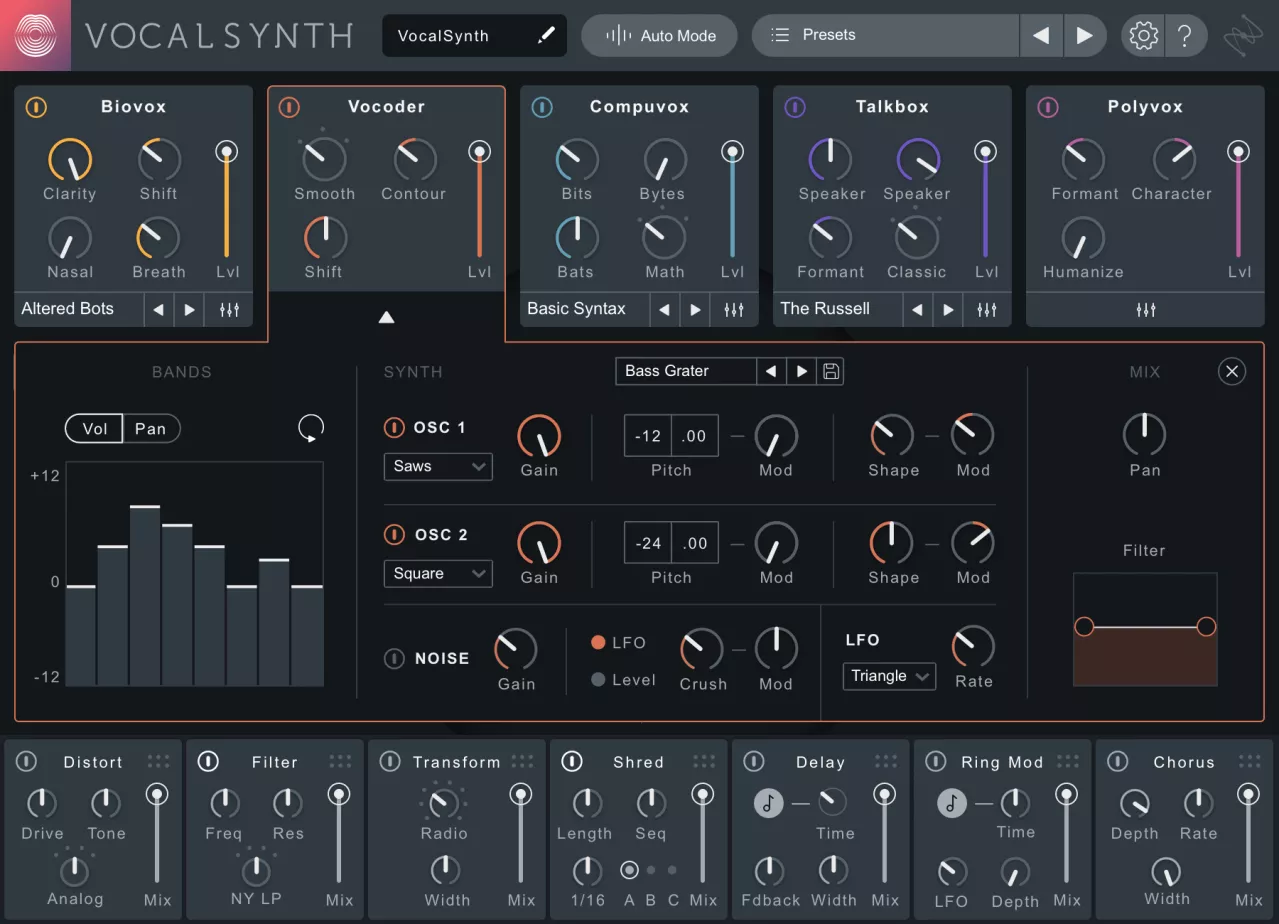
2. Waves OVox
Waves OVox OVox is a versatile vocoder plugin known for its high-quality sound and intuitive interface. It's perfect for both beginners and experienced producers.
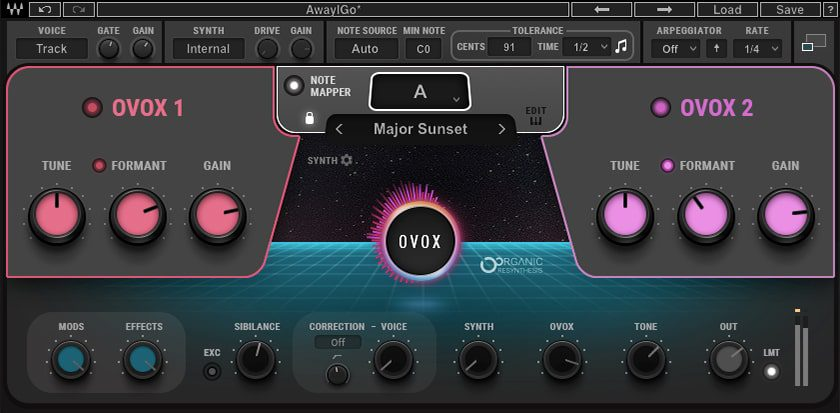
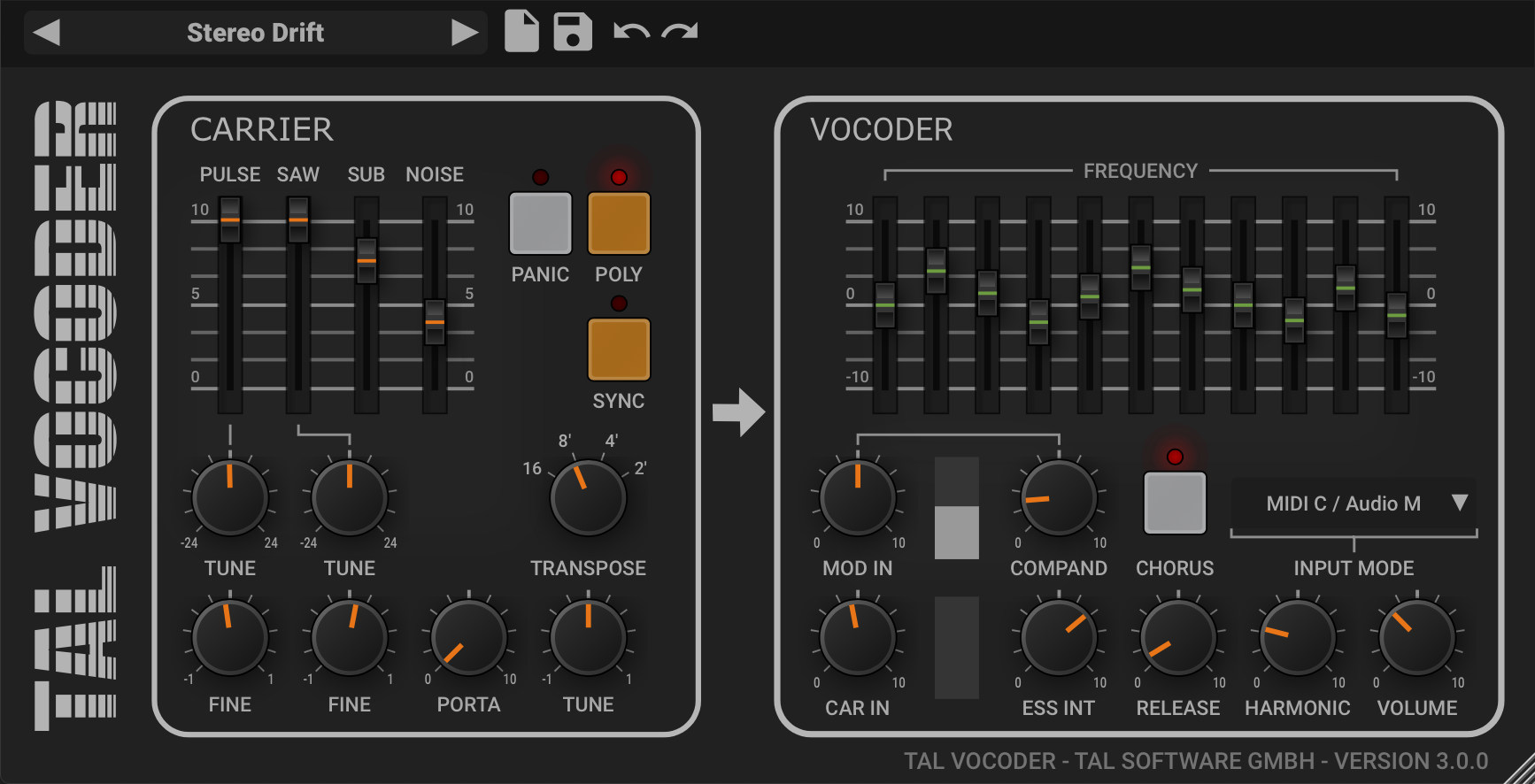
3. TAL-Vocoder
TAL-Vocoder TAL-Vocoder is a free plugin that delivers impressive results. It's simple to use and great for those on a budget.
Best Hardware Vocoders
Prefer hardware? The Korg MicroKorg and Roland VP-03 are great picks for hardware vocoders.
1. Korg MicroKorg
Korg MicroKorg The MicroKorg is a classic synth with a built-in vocoder. It's compact, affordable, and offers a unique analog sound.
2. Roland VP-03
Roland VP-03 The VP-03 is a boutique version of the legendary VP-330 vocoder. It's perfect for producers who want that vintage Roland sound.
Vocoder Software: Online vs Offline
Vocoder Online Tools
If you're looking for a quick and easy way to apply vocoder effects, there are several online tools available. Websites like Vocaroo offer basic vocoding features that you can use directly in your browser.
Offline Vocoder Software
For more control and higher quality, offline vocoder software is the way to go. Plugins like iZotope VocalSynth 2 and Waves OVox are industry standards and offer a wide range of features.
Pro Tips for Vocoding
- Experiment with Different Carriers: Try using different synthesizers or even acoustic instruments as your carrier signal to create unique sounds.
- Layer Vocals: Stack multiple vocal tracks with slight variations in pitch and timing to create a richer, more complex sound.
- Automate Parameters: Use automation to dynamically change vocoder parameters throughout your track, adding movement and interest.
Recap
- Vocoders blend two signals (modulator and carrier) to create robotic effects
- More frequency bands mean better quality but higher CPU usage
- arameter automation adds movement and interest to vocoded sounds
Final Words
The vocoder is a great tool to add extra creativity to your music. You can go for analog hardware, digital plugins, or online tools but first understand the parameters of a vocoder. Try different carriers and layer your vocals to add depth. Automate those parameters for some dynamic flair in your tracks – this help you get the sound you're looking for.





Comments